
In
convex geometry
In mathematics, convex geometry is the branch of geometry studying convex sets, mainly in Euclidean space. Convex sets occur naturally in many areas: computational geometry, convex analysis, discrete geometry, functional analysis, geometry of num ...
and
vector algebra In mathematics, vector algebra may mean:
* Linear algebra, specifically the basic algebraic operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication; see vector space.
* The algebraic operations in vector calculus, namely the specific additional stru ...
, a convex combination is a
linear combination of
points (which can be
vector
Vector most often refers to:
*Euclidean vector, a quantity with a magnitude and a direction
*Vector (epidemiology), an agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen into another living organism
Vector may also refer to:
Mathematic ...
s,
scalars, or more generally points in an
affine space
In mathematics, an affine space is a geometric structure that generalizes some of the properties of Euclidean spaces in such a way that these are independent of the concepts of distance and measure of angles, keeping only the properties relate ...
) where all
coefficients
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of a polynomial, a series, or an expression; it is usually a number, but may be any expression (including variables such as , and ). When the coefficients are themselves ...
are
non-negative
In mathematics, the sign of a real number is its property of being either positive, negative, or zero. Depending on local conventions, zero may be considered as being neither positive nor negative (having no sign or a unique third sign), or it ...
and sum to 1.
In other words, the operation is equivalent to a standard
weighted average
The weighted arithmetic mean is similar to an ordinary arithmetic mean (the most common type of average), except that instead of each of the data points contributing equally to the final average, some data points contribute more than others. The ...
, but whose weights are expressed as a percent of the total weight, instead of as a fraction of the ''count'' of the weights as in a standard weighted average.
More formally, given a finite number of points
in a
real vector space
Real may refer to:
Currencies
* Brazilian real (R$)
* Central American Republic real
* Mexican real
* Portuguese real
* Spanish real
* Spanish colonial real
Music Albums
* ''Real'' (L'Arc-en-Ciel album) (2000)
* ''Real'' (Bright album) (2010) ...
, a convex combination of these points is a point of the form
:
where the real numbers
satisfy
and
[
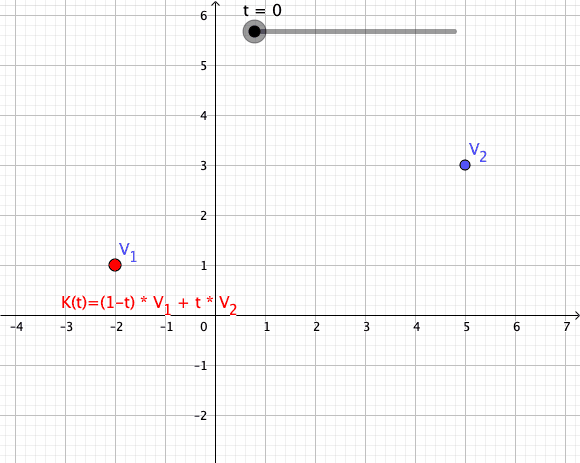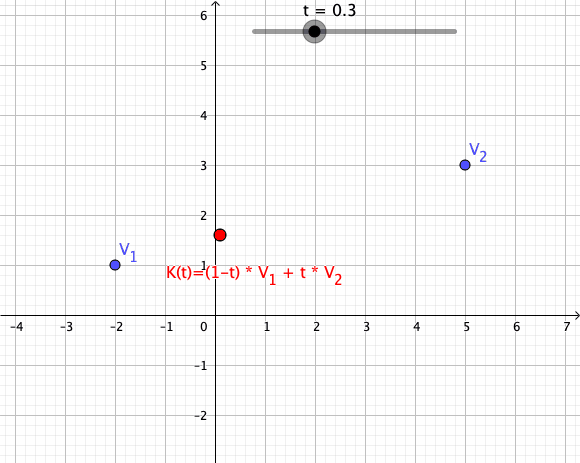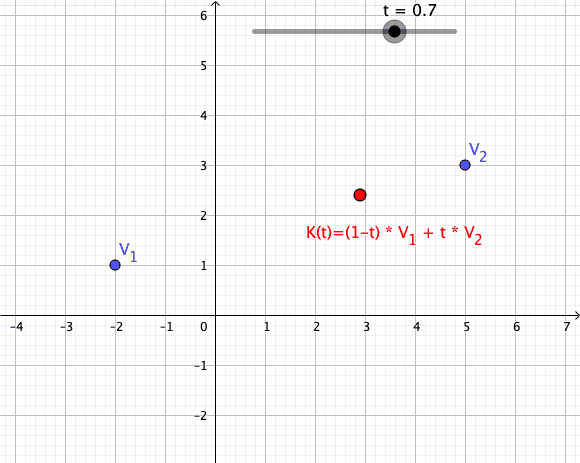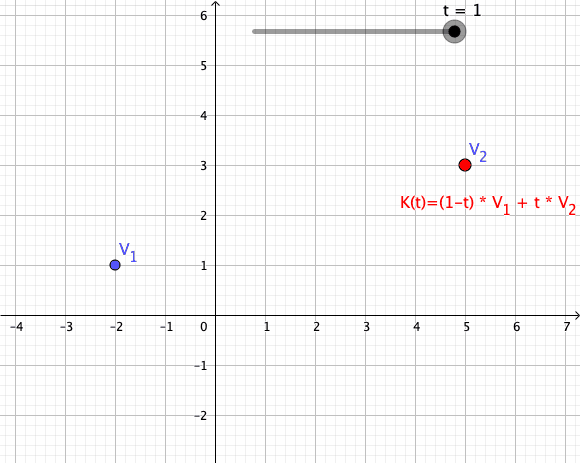
As a particular example, every convex combination of two points lies on the ]line segment
In geometry, a line segment is a part of a straight line that is bounded by two distinct end points, and contains every point on the line that is between its endpoints. The length of a line segment is given by the Euclidean distance between ...
between the points.[
A set is ]convex
Convex or convexity may refer to:
Science and technology
* Convex lens, in optics
Mathematics
* Convex set, containing the whole line segment that joins points
** Convex polygon, a polygon which encloses a convex set of points
** Convex polytope ...
if it contains all convex combinations of its points.
The convex hull
In geometry, the convex hull or convex envelope or convex closure of a shape is the smallest convex set that contains it. The convex hull may be defined either as the intersection of all convex sets containing a given subset of a Euclidean space ...
of a given set of points is identical to the set of all their convex combinations.[
There exist subsets of a vector space that are not closed under linear combinations but are closed under convex combinations. For example, the interval ]

 In
In

 In
In